Vyux F

Answered Y Y U V With A 5 4 X X U V Bartleby
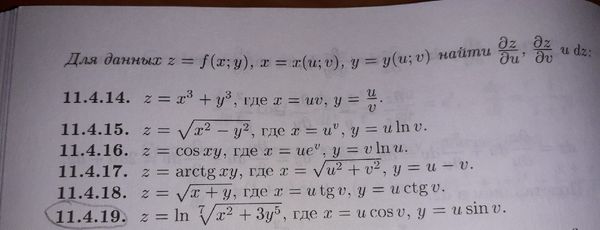
11 4 19 Dlya Dannyh Z F X Y X X U V Y U V Najti Dz Du Dz Dv I Dz

16 Krivolinejnye Koordinaty Zamena Peremennyh V Differencialnyh Vyrazheniyah Pdf Skachat Besplatno

Probability And Statistical Inference 9 Th Edition Chapter
Let U X And V X Satisfy The Differential Equations Du Dx P X U F X And Dv Dx P X V G X Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
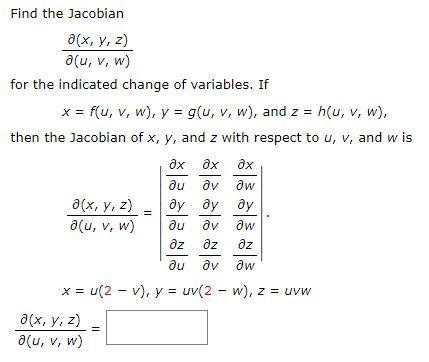
Solved Find The Jacobian X Y Z A U V W For The Ind Chegg Com
2 x145, #15 (5 points) Suppose that f is a differentiable function of xand y, and that g(u;v) = f(eu sinv;eu cosv) Suppose also that g(0;0) = f(1;2) = 6, f x(1;2) = 2, and f y(1;2) = 5 Find g u(0;0) and g v(0;0) Solution We have x(u;v) = eu sinv, y(u;v) = eu cosv, and we note that x(0;0) = 1, y(0;0) = 2 We compute g u(0;0) = f x(1.

Vyux f. ¶ 4 Let Y be compact and Hausdorff Prove that f X → Y is continuous if and only if the graph {(x, f(x)) x ∈ X} is a closed subset of X ×Y Solution If Y is compact then the projection X ×Y → X is closed Indeed, if A is a closed subset of X ×Y and x is not in the projection of A onto X, then apply tube lemma to {x}×Y. Question 3 = , Functions, F = F(x,y), X = X(u, V),y X(u, V),y = Y(u, V)) Are All C Binaryvariable Functions Given The Following Information;. F(x(t);y(t)) = @f @x x0(t) @f @y y0(t) = rf~x0(t) and @f @u (x(u;v);y(u;v)) = f x @x @u f y @y @u Example De ne P= f(x;y) x= st;y= s=t Find @P @t Example f(x;y) is a function of x;y Let g= f(uv;u=v) Compute g uu;g uv;g vv Application 1 Polar coordinate x= rcos ;y= rsin Example If you know @f=@r= 3;@f=@ = 6 at Cartesian point (4;3.
Provided to YouTube by Parlophone UKUFO · ColdplayMylo Xyloto℗ 11 Parlophone Records Ltd, a Warner Music Group CompanyMastering Engineer Bob LudwigAss. X = au x (1) and v y = au y (2) Using (1) and the CR equation u x = v y, we get v x = av y Into this equation, we plug (2) and obtain v x = a2u y Into this equation, plug the CR equation u y = v x, and we obtain v x = a2v x If a6= 0, then v x = 0 and thus by the preceding equations, all partial derivatives of uand vare 0 Thus, by Theorem. Dec 14, 10 · Express f(x,y,z) = yz in terms of u and v and evaluate \\int\\int_S f(x,y,z)dS This is supposed to be simple but I really don't know how to do this I rewrote f(x,y,z) = yz as x = g(y,z) so then \\Phi(y,z) = (y,z, x) Tx = (0,0,1) and Ty=(1,0,0) and their corss product, n, is Am I even.
F(x,y,z)dS = ZZ D f(x,y,g(x,y)) q 1g2 x g2y dA • Terminology a unit normal vector for the surface is n = r u(u,v)×r v(u,v) r u(u,v)×r v(u,v);. An oriented surface has a continuous n;. Chain Rule Case 1Supposez = f(x,y)andx = g(t),y= h(t) Based on the one variable case, we can see that dz/dt is calculated as dz dt = fx dx dt fy dy dt In this context, it is more common to see the following notation fx = @f @x The symbol @ is referred to as a “partial,” short for partial derivative 2 Chain Rule Case 2.
2y;1idxdy= ZZ x2y2 1 2y2 x2 y2 dxdy Let us pass to polar coordinates Z 2ˇ 0 Z. The change of variables theorem (which you learned in Math 57) says 1 Z Z A f(x,y)dydx = Z Z B f(x(u,v),y(u,v))J(u,v)dudv (1) Now if f = fX,Y is the pdf of (X,Y), the left side of (1) is P((X,Y) ∈ A) = P(H(X,Y) ∈ H(A)) = P((U,V) ∈ B). ∂(x,y) ∂(u,v) = u x xv yu yv , g(u,v) = f(x(u,v),y(u,v)), it looks as if the essential equations we need are the inverse equations () x = x(u,v), y = y(u,v) rather than the direct equations we are usually given (21) u = u(x,y), v = v(x,y) If it is awkward to get () by solving (21) simultaneously for x and y in terms of u and v,.
In singlevariable calculus, we found that one of the most useful differentiation rules is the chain rule, which allows us to find the derivative of the composition of two functions The same thing. Chain Rule Given the function {eq}z = f(x(u,v),y(u,v)) {/eq}, where the x and y are functions of the variables u and v, the partial derivative {eq}z_v {/eq} is calculated by applying the chain. *Response times vary by subject and question complexity Median response time is 34 minutes and may be longer for new subjects Calculus An Applied Approach (MindTap Course List) Finding a Limit Graphically In Exercises 2330, use the graph to find the limit (if it exists) If the limit do.
Solution for Evaluate the surface integral (x y z) dS, S is the parallelogram with parametric equations x = u v, y = u – v, z = 1 2u v, 0 sus 9, 0 sv. • If F is a vector field on an oriented surface S, the surface integral of F. Y;x2 y2ih 2x;.
FdS for F = 2yjzk, where Sis the part of the paraboloid z= x y2 below the plane z= 1 with upward orientation The surface is the graph of the function g(x;y) = x2 y2 It follows that dS = h 2x;. Find div F for F(x, y, z) = (x2 y2)i (xz)j (yz)k 2z − x − y 2x 3y 2z 2x y y x Study Guide for Stewart's Multivariable Calculus, 8th Precalculus or Calculus In Exercises 36decide whether the problem can be solved using precalculus or whether. X= v y, u y= −v x (16) The boxed pair of equations above are known as the CauchyRiemann equations If these hold at a point zthen f(z) is said to be differentiable atz There is no such requirement in single variable calculus Moreover the CR equations bring us to a further idea regarding differentiation in the complex plane.
E 1 D R Q 7 P O H M 7 L K N M J L K J I 7 H G 1 C 2 G F 9 U T S V U X W U Y X \ X Z Y _ W _ ^ U Y Y a ` V W e d c _ b U X U e Y U X S f g Y i h U X b e Y g Y _ _ j Y k V Y W l i i V V _ W U m. Chain Rule Use chain rule of partial derivative to solve the given problem If {eq}z=f(x,y) \ and \ x=g(t) , y= h(t) {/eq} then {eq}\displaystyle \frac{{dz}}{{dt. V x vy uj u v And, the area of a cross section of region S is A S = u v So, the the scaling factor that relates the two is jx uy v x vy uj We often write this as the determinant of a matrix, called the Jacobian Matrix De nition The Jacobian Matrix is @(x;y) @(u;v) = x u x v y u y v Jason Aran Change of Variables & Jacobian June 3, 15 15 /.
A closed surface with an outward pointing n has a positive orientation;. Let w= f(x;y;z) be a function of three variables Introduce a new object, called thetotal di erential df= f xdx f ydy f zdz Formally behaves similarly to how fbehaves, fˇf x x f y y f z z However it is a new object (it is not the same as a small change in fas. In this equation, both f (x) f (x) and g (x) g (x) are functions of one variable Now suppose that f f is a function of two variables and g g is a function of one variable Or perhaps they are both functions of two variables, or even more How would we calculate the derivative in these cases?.
Where N~ is the upward unit normal For the downward unit normal, multiply by 1 Example Find the ux of F~(x;y;z) = hey;yex;x2yiacross the part of the paraboloid z= x 2 y that lies above the square 0 x 1, 0 y 1 and has upward orientation Applying the previous theorem, the ux of F~across Sis ZZ S F~ ydS. E y X I y F S y D V y U P a ti nadie te valora B y F G y M N y H D y O J y A (siempre serán la mejor) R y M C y S L y Y J y A (Insisto, es la mejor) Perfect Couples J Y A E and X I and F S and D V y U P to you no one values you B and F G and M N and H D Y O J and A (always be the best) R Y M C and S L Y Y Y Y J and A (I insist, is the best). • Vector surface integral x S (F · n) dS = x S F · d S = x D F (G (u, v)) · N (u, v) dudv • The surface integral of a vector field F over S is also called the flux of F through S If F is the velocity field of a fluid, then s S F · d S is the rate at which fluid flows through S per unit time.
Using the CauchyRiemann equations, show that if f and f are both holomorphic then f is a constant Solution Let f = uiv,so f = u iv Since they are holomorphic, we can use the CauchyRiemann equations ux = vy and ux = vy) ux = vy = 0 uy = vx and uy = vx) uy = vx = 0 Therefore ux = uy = 0so uis constant, and similarly vx = vy = 0so v is. Suppose f is a differentiable function of x and y , and g ( u , v ) = f ( e u sin v , e u cos v ) Use the table of values to calculate g u (0, 0) and g v (0, 0) Buy Find launch. F(x)dx= Z f(g(u)) dx du du The Jacobian is what generalizes dx du in the above formula We begin with the change of variable theorem for double integrals We then look at several examples to see how one can bene–t from a change of variable These bene–ts.
F~dS~= ZZ D P @g @x Q @g @y R dA;. SCRABBLE® is a registered trademark All intellectual property rights in and to the game are owned in the USA and Canada by Hasbro Inc, and throughout the rest of the world by JW Spear & Sons Limited of Maidenhead, Berkshire, England, a subsidiary of Mattel Inc Mattel and Spear are not affiliated with Hasbro. F(x;y)dxdy = ZZ D⁄ f(x(u;v);y(u;v)) fl fl fl fl @(x;y) @(u;v) fl fl fl fldudv We proved this for a linear map if f =1 when it says that the area of D is the area of D⁄ times the Jacobian determinant which is the determinant of the linear map The general case follows by dividing up D⁄ into smaller sets on which we can approximate.
Suppose that f is a differentiable function with fx(0, 0) = 6 and fy(0, 0) = 2 Let w(u, v) = f (x(u, v), y(u, v)) where x = 5 cos u 4 sin v and y = 4 cos u sin v. Solution for Let x = u cos³ (v), y = u sin³ (v) (a) Sketch the region D in the xyplane corresponding to 1 < u < 3, T. 2y;1i The integral is equal to ZZ x2y2 1 h0;.
Example 5 Using the change ZoZ f coordinates u = x2 − y2, v = y/x of Example dxdy 3, supply limits and integrand for , where R is the infinite region in the first x2 R quadrant under y = 1/x and to the right of x2 −y2 = 1 Solution We have to change the integrand, supply the Jacobian factor, and put in the right limits. Thereom $$\{x,y\}=\{u,v\} \rightarrow \biggx=u \wedge y=v \vee x=v \wedge y=u\bigg$$ Proof (by Contradiction) $$ \begin{align} (x \neq u \vee y\neq v)\wedge.

Section 22 Sufficient Conditions For Differentiability Pages 1 8 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Get Answer Help Anyone Please Solves This I Still Cant Figure It Out Why Transtutors

Cauchy Riemann Equation Algebra Teaching Mathematics

14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts
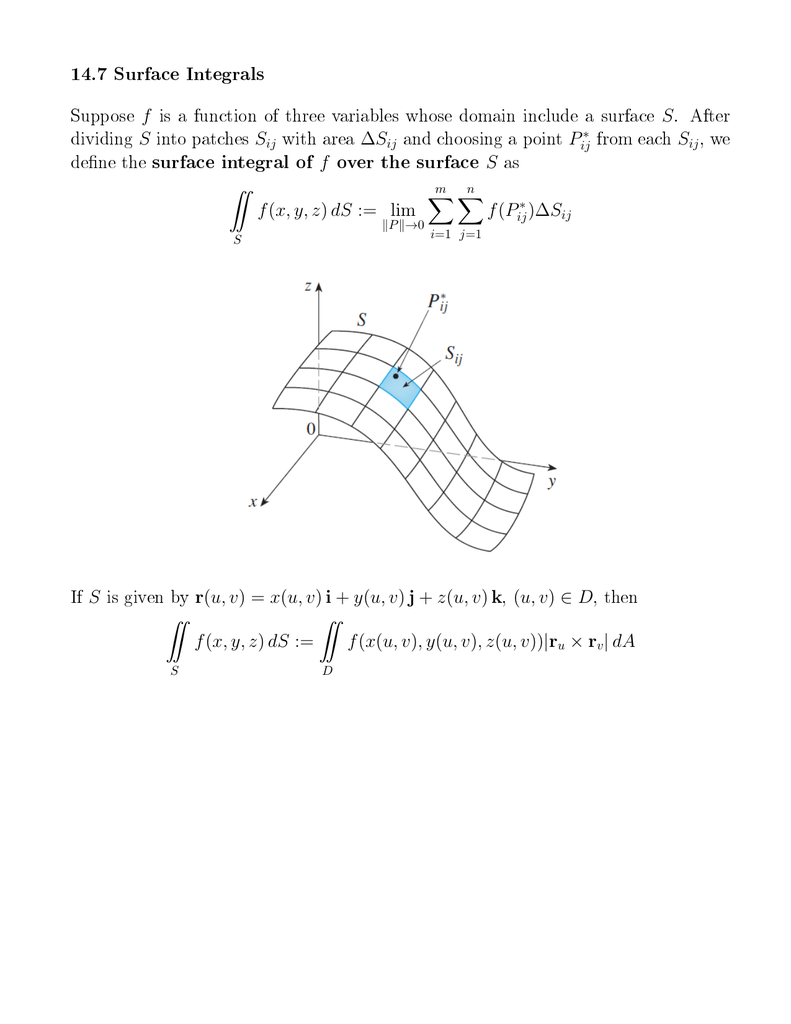
14 7 Surface Integrals

Hw2sol

F X 1 X K H X N F X 1 X K X N Pdf Free Download

Find F Z U X Y Iv X Y With U Or V As Given Check By The Cauchy Riemann Equations For Analyticity U Xy Homework Help And Answers Slader

Surface Integrals With Parameterized Surface Part 1 Youtube
Answered F X Y X I V Y 2 4 3 Bartleby

Help In Proof Of Frac Partial U V Partial X Y Frac Partial X Y Partial U V 1 Mathematics Stack Exchange

Gec2 Tutorials Functions Of Several Variables

Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu

Exercise Partial Derivatives Studocu

If U And V Are Two Functions Of X Then Prove That Int Uv Dx U Int V Dx Int Dudxint V Dx Dx
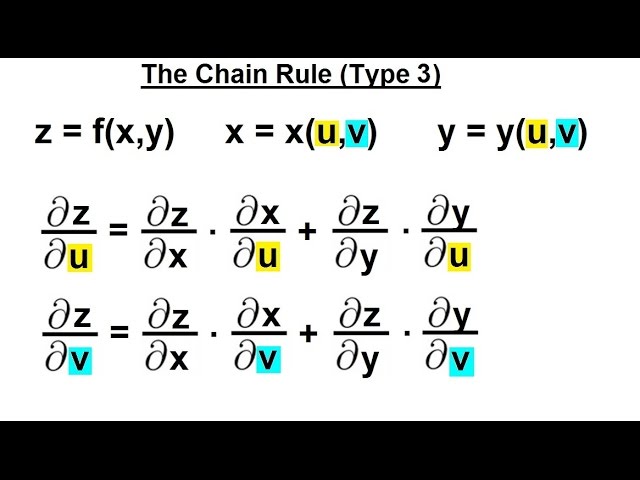
Calculus 3 Partial Derivative 28 Of 50 The Chain Rule Type 3 Youtube

Solved 1 Draw The Tree Diagram For The Chainrule And Wr Chegg Com

Probability And Statistical Inference 9 Th Edition Chapter

Solved For An Analytic Function F X Iy U X Y Iv X Y U Is Given By Self Study 365

Displacement Field U X Y And V X Y Between An Initial Image And A Download Scientific Diagram

2 Functional Dependence Differential Calculus Functions And Mappings
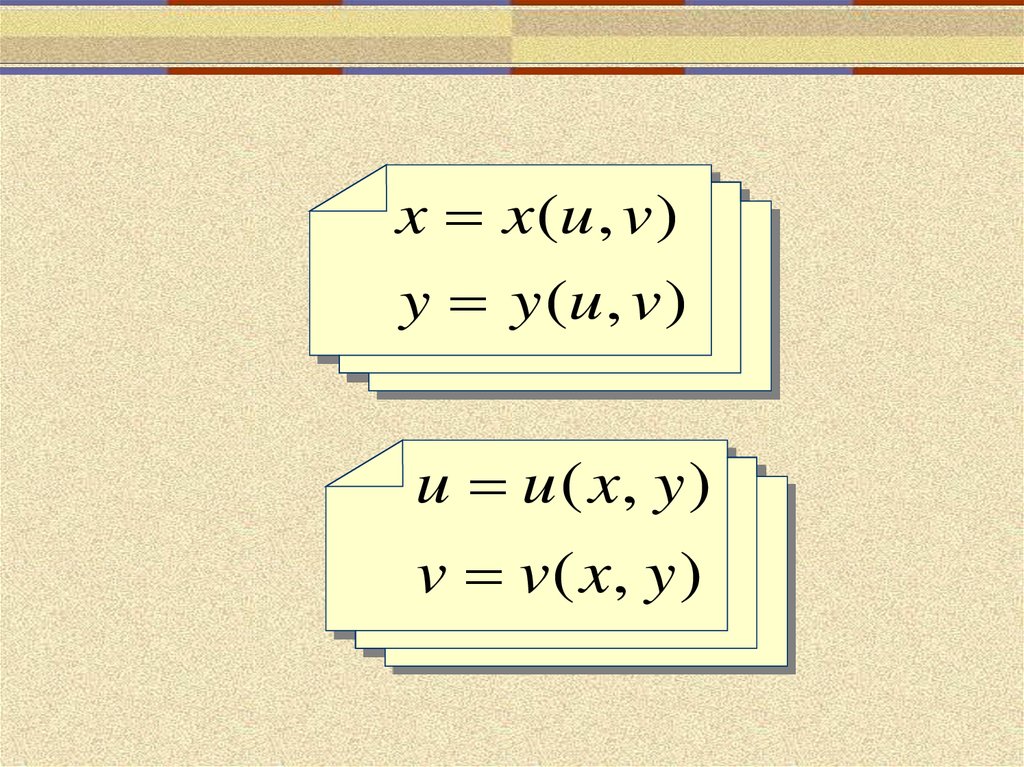
Zamena Peremennoj V Dvojnom Integrale Online Presentation

Displacement Field U X Y And V X Y Between An Initial Image And A Download Scientific Diagram

Differentiability Of Complex Functions Contents Pdf Free Download

7 Show That The Following Functions U X Y Monic Functions V X Y And Determine F Z U X Y Iv X Y Are Harmoni Homeworklib
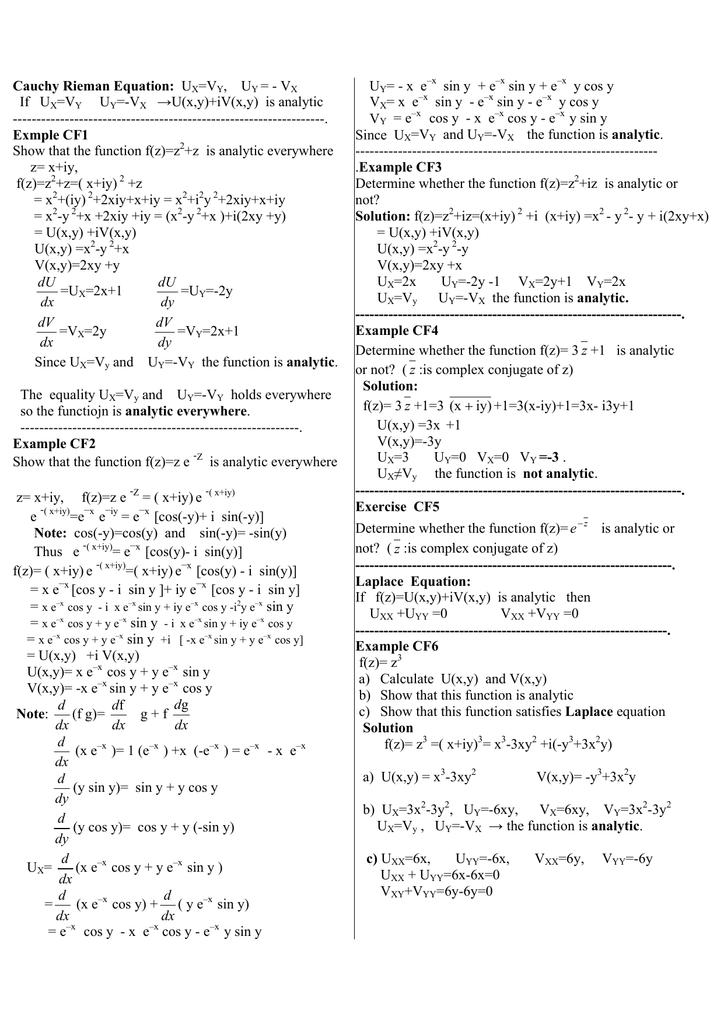
Ux Vy Uy Vx If Ux Vy Uy
Osa Displacement And Strain Mapping For Osteocytes Under Fluid Shear Stress Using Digital Holographic Microscopy And Digital Image Correlation

Multi Function Partial Derivatives Confusion Mathematics Stack Exchange

Dm6103 Tutorial 03 Virtual Reality Ntu Studocu

Index Of N10 2 Kurs Matan Ikramov17 Png

Dream Idea Plan Implementation 1 Complex Variables Present

2 Functional Dependence Differential Calculus Functions And Mappings
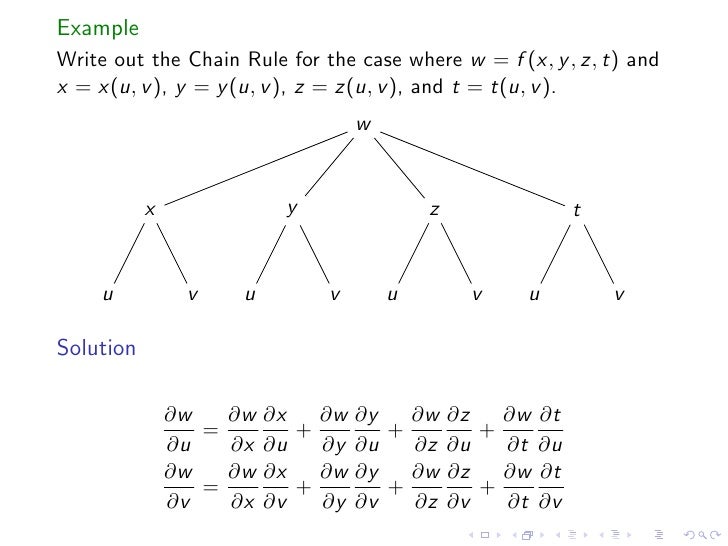
Lesson 23 The Chain Rule

Calameo Alphabet In English
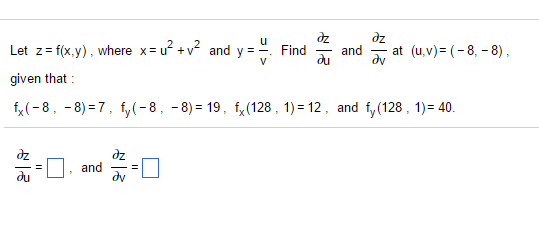
Solved Let Z F X Y Where X U 2 V 2 And Y U V Chegg Com
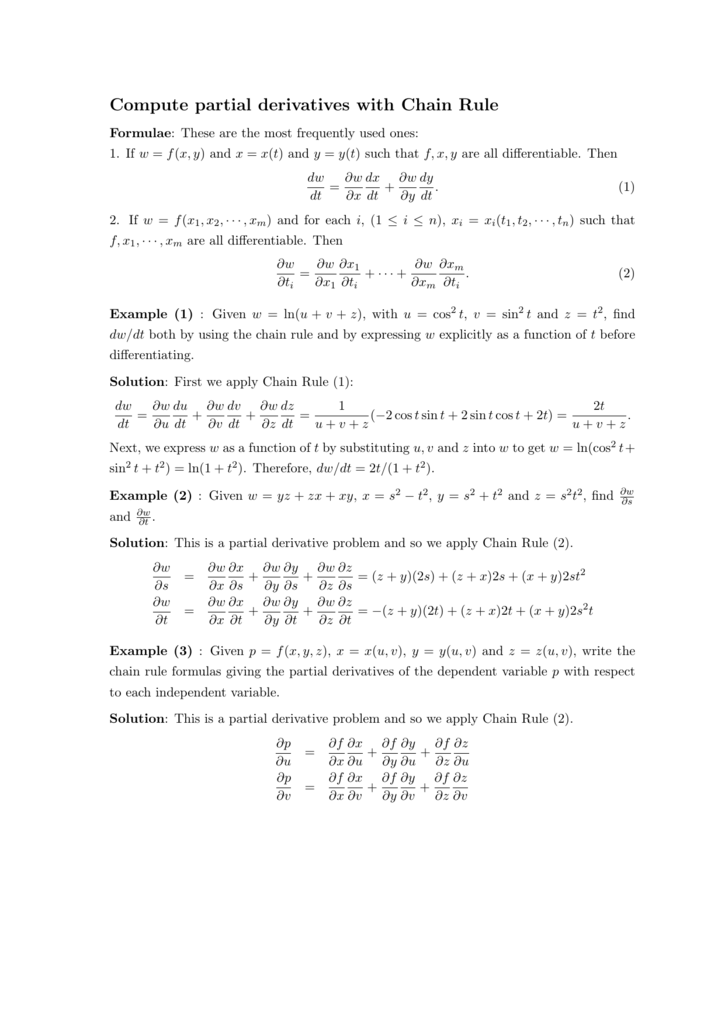
Compute Partial Derivatives With Chain Rule
Plotting Vector Fields In Python Ajit Kumar

14 5 The Chain Rule For Multivariable Functions Mathematics Libretexts
Najti Proizvodnye Funkcij Dvuh Peremennyh Dz Dx Dz Dy Z U 2 Sqrt U V U X 2y V Xy Shkolnye Znaniya Com

Dream Idea Plan Implementation 1 Complex Variables Present
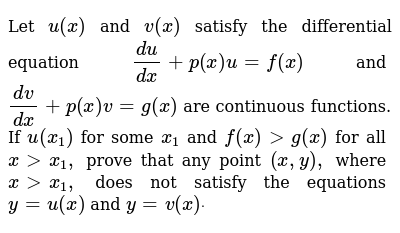
Let U X And V X Satisfy The Differential Equation D U

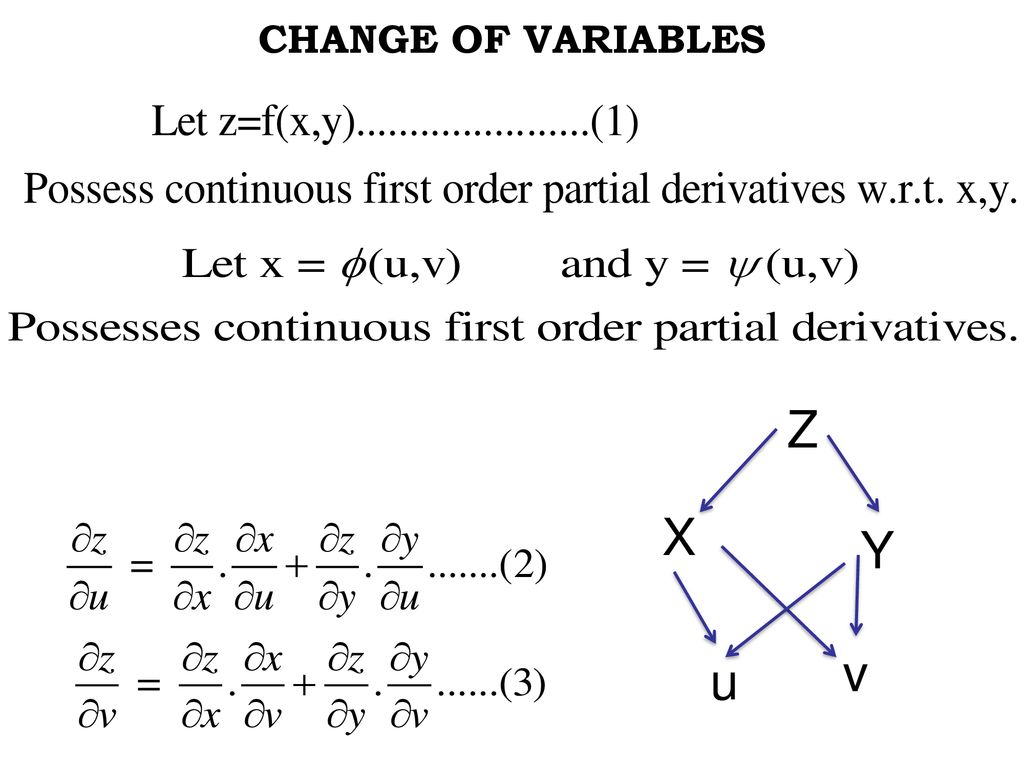
Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download

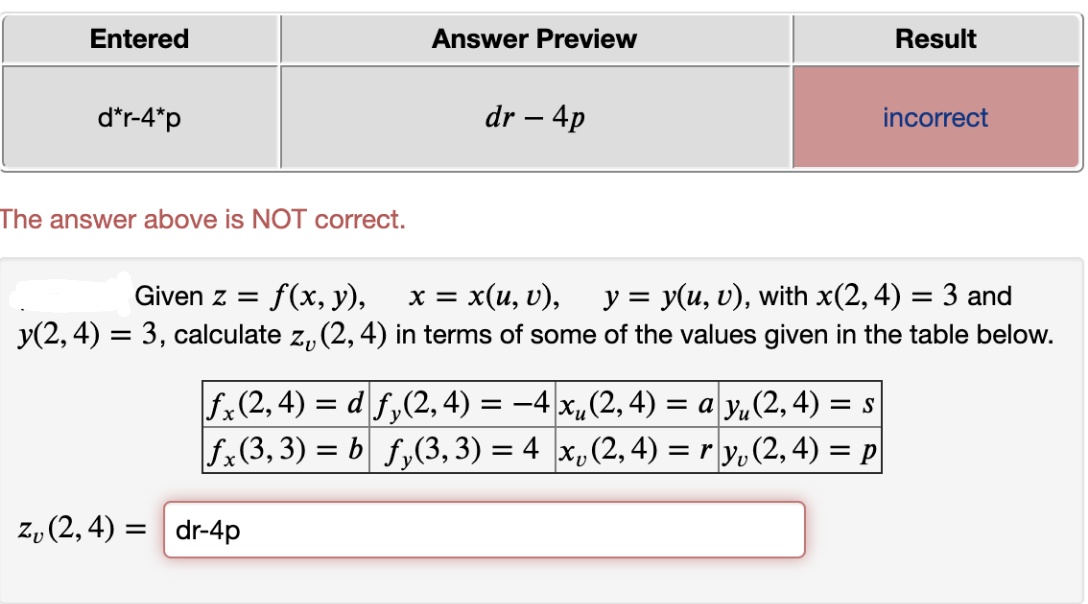
Given Z F X Y X X U V Y Y U V With X 5 2 3 Y 5 2 1 Calculate Z U 5 2 In Terms Of Some Of The Values Given In The Table Below F X 5 2 A F Y 5 2 2 X U 5 2

Midterm Exam 1 With Answers Complex Variable For Science And Engineers Math 463 Docsity

If Y Int U X V X F T Dt Let Us Define Dy Dx In A Diff
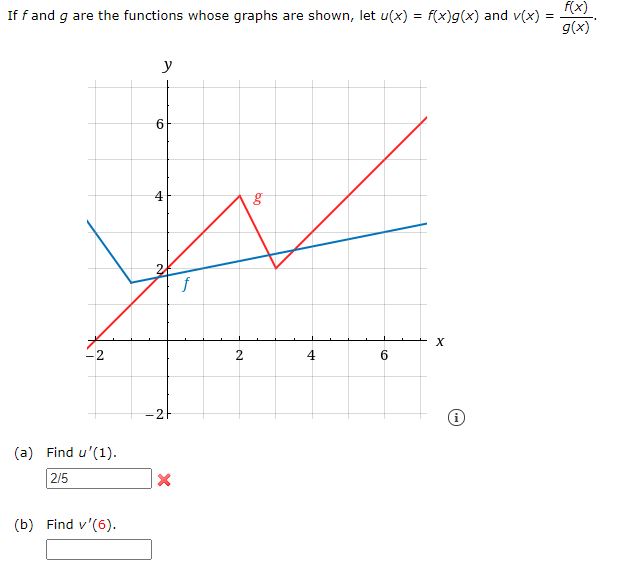
Answered F X If F And G Are The Functions Whose Bartleby

Why V 1 2 Is F Distribution With 2 2 Degree Of Freedom Mathematics Stack Exchange
Prezentaciya Na Temu P 5 Svyaz Analiticheskoj Fkp I Garmonicheskoj Funkcii Dvuh Dejstvitelnyh Peremennyh Skachat Besplatno I Bez Registracii

Sqrt2 Iiff U Xyzt Dfracf Tr See How To Solve It At Qanda
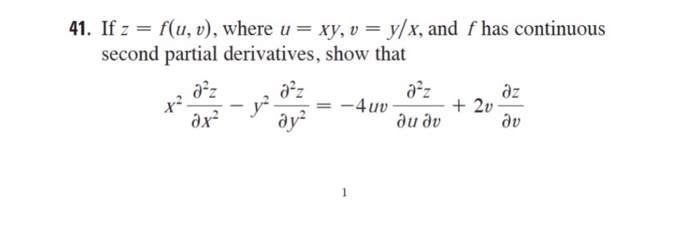
Solved If Z F U Y Where U Xy V Y X And F Has Co Chegg Com
Find An Analytic Function F Z U Iv Whose U V X X 2 Y 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
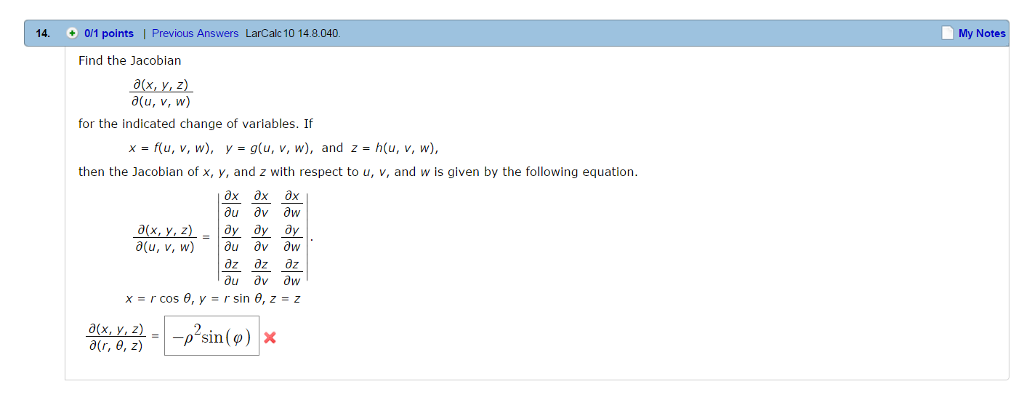
Solved Find The Jacobian Partial Differential X Y Z P Chegg Com

Chapter 2 First Order Differential Equations Eut 102

Find The Value For V X Y In The Function F X Iy U X Y Iv X Y With U X Y Log X 2 Y 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
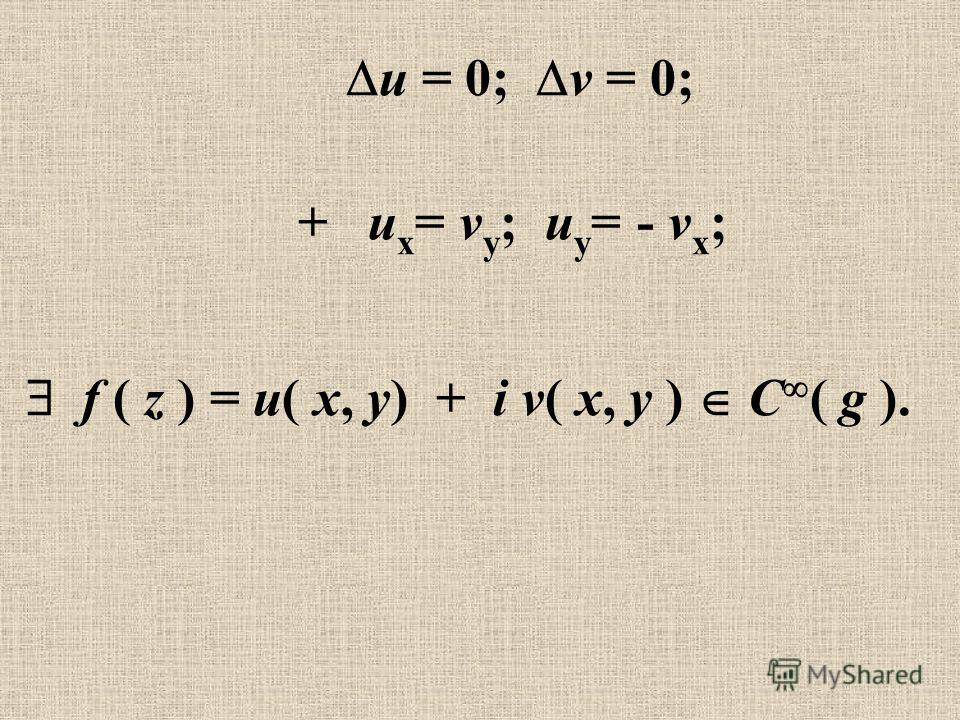
Prezentaciya Na Temu P 5 Svyaz Analiticheskoj Fkp I Garmonicheskoj Funkcii Dvuh Dejstvitelnyh Peremennyh Skachat Besplatno I Bez Registracii

Consider The Steady State Heat Transfer Or Other Phenomenon In A Square Region Shown In Figure P8 23 The Governing Equation Is Given By X K U X Y K U Y F0

Differencialnye Uravneniya Prezentaciya Onlajn

Solved P F V W V X Y Z T W X Y Z T P Chegg Com
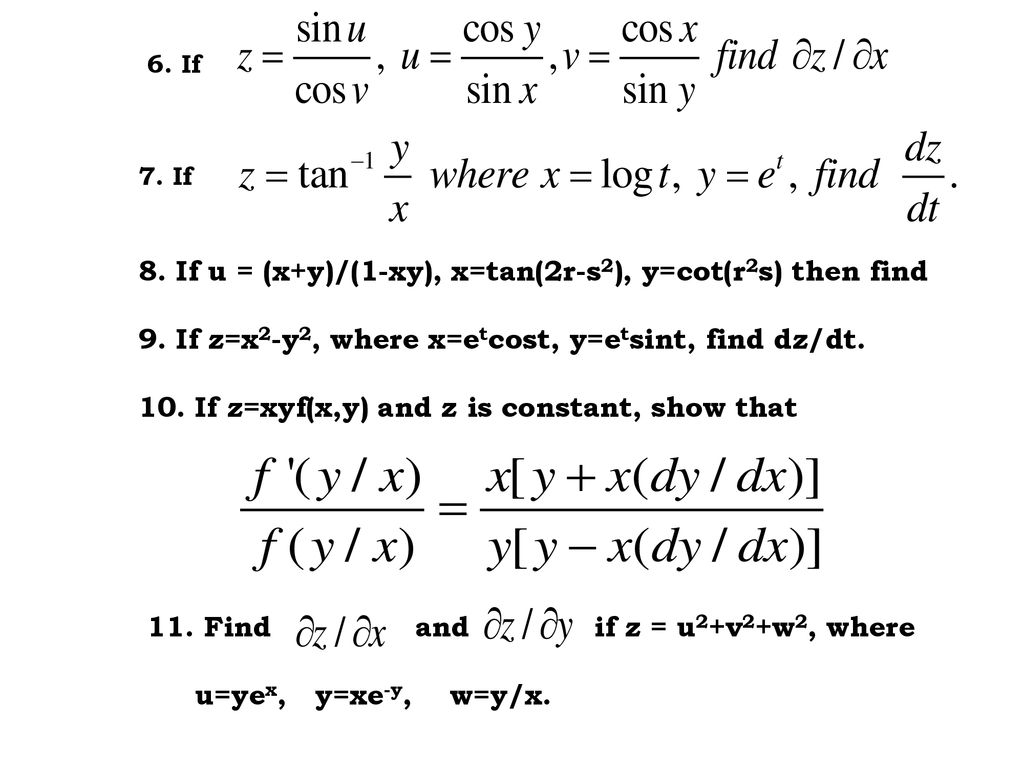
Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download
Ppt Jpeg Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5110
Differentiation Of Composite Function Let Z F X Y Possesses Continuous Partial Derivatives And Let X G T Y H T Possess Continuous Ppt Download

If W F U V Where U X Y V X Y Show Dw Dx Dw Dy 2dw Du Brainly In

Variablecomplejaysusaplicaciones 7maedicion Churchill Solucionario Co

Inequalities For The Riemann Stieltjes Integral Of S Dominated Integrators With Applications I Tema Nauchnoj Stati Po Matematike Chitajte Besplatno Tekst Nauchno Issledovatelskoj Raboty V Elektronnoj Biblioteke Kiberleninka

The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example Ppt Download

Advanced Engineering Mathematics Pages 651 700 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Chastotnye Metody Uluchsheniya Izobrazhenij Fure Analiz Online Presentation
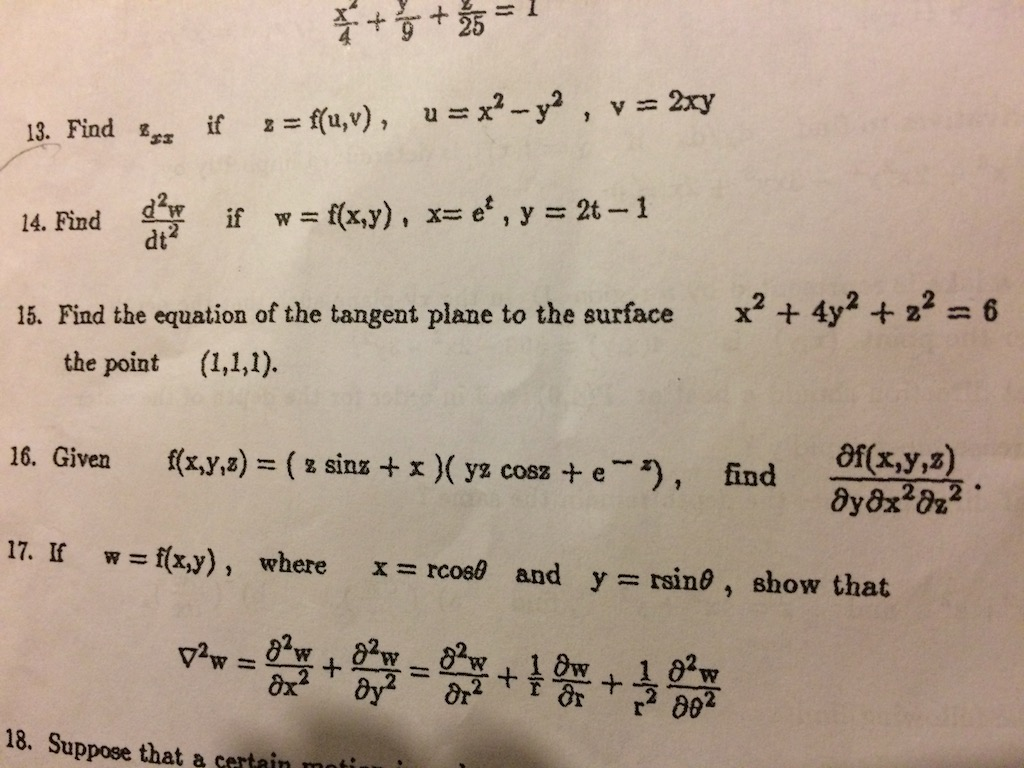
Solved Find Z Xx If Z F U V U X 2 Y 2 V 2xy F Chegg Com

Pohidna Skladnih Funkciyi Y F H X Znahoditsya Za Formuloyu A Yx Yx Ux B Yx Yu Ux V Shkolnye Znaniya Com

Proizvodnaya Prezentaciya Doklad
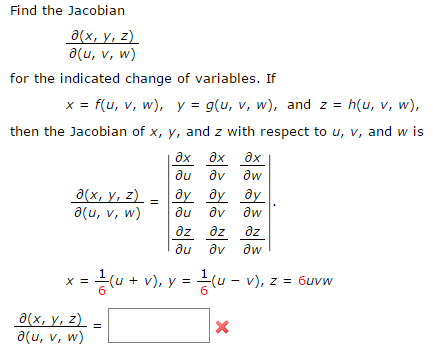
Solved Find The Jacobian Partial Differential X Y Z P Chegg Com
Let X And Y Be Iid N 0 1 Rv S Define U Xy And V X Y Note Uv X2 And U V Y2 Hence We Have The Restriction D

1 Vytah

Vector Analysis By Alimkanwalimtinaa Issuu

Dhl Pending Notificationdhl Awb ad Online Presentation

Solved Given The Function F X Y With X U V Au Bv Chegg Com
Solved The Joint Pdf Of X Y And Z Is Given By F X Y Z 8xy E Z For 0x Y1 Z 0 0 Otherwise What Is The Joint Pdf Of U X Y And V Y Course Hero

Solved 1 Point Given Z F X Y X X U V Y Y U Chegg Com

The Derivative Rules For Multivariable Functions Stated Theorem 10 On Page 151 Are Analogous To Derivative Rules From Single Variable Calculus Example 1 Page 152 Illustrates The Quotient Rule Reca



